
What’s New in Nail Anatomy? The Latest Facts! Schoon Scientific
The nail functions by protecting the digits and contributing to tactile sensation. Understanding nail anatomy is not only essential for understanding physiology but also comprehending the pathophysiology behind many nail presentations. Clinically, many cutaneous and systemic diseases can manifest on the nails. While a thorough history and physical can often correlate nail findings with their.

5,233 Nail Anatomy Images, Stock Photos, 3D objects, & Vectors
It produces most of the volume of the nail and the nail bed. The germinal matrix (the nail matrix) and the nail root are related. The matrix lies beneath the skin, at the inner edge of the nail plate, and is responsible for most of a nail's growth. It's where new cells grow and then advance forward to form the nail, until it reaches the outer.

Diagram Typical Nail +9000 Pendant Lighting Modern
Structure. The nail unit includes the nail plate and supporting structures. This section explains the anatomy of the nail unit and histologic findings of each region.. Ink, suture, or an accompanying diagram can facilitate communication of the orientation. Processing a nail biopsy is more challenging than a standard skin biopsy. The specimen.
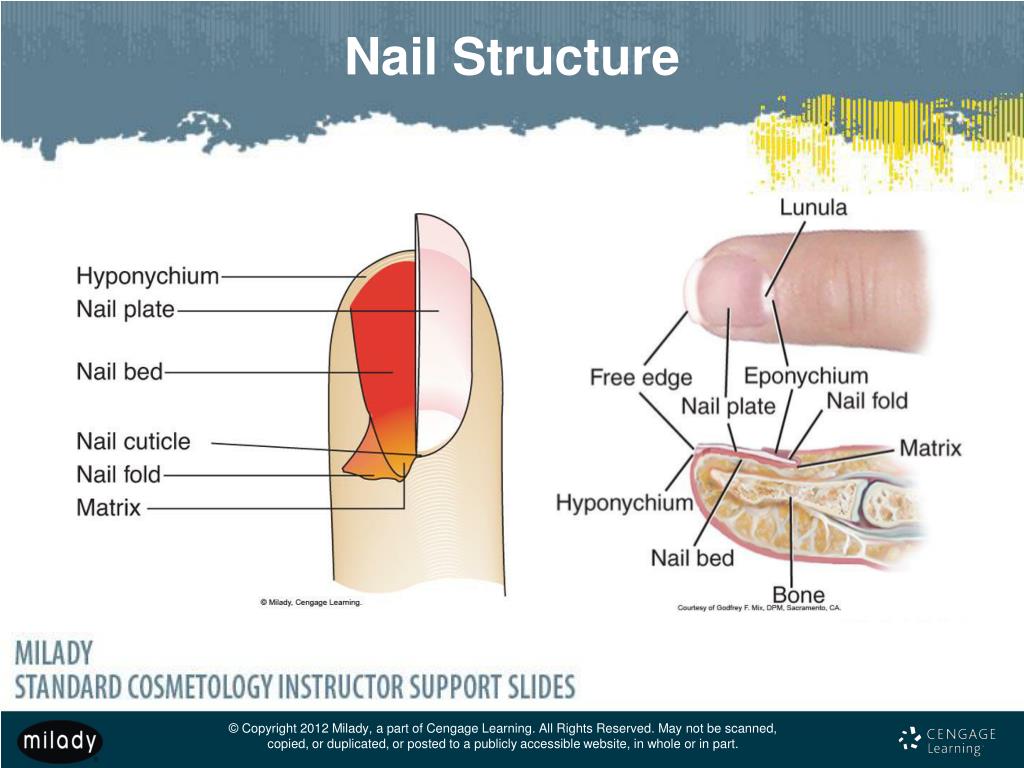
PPT Chapter 9 Nail Structure and Growth PowerPoint Presentation, free
The nail plate emerges from the proximal nail fold and is bordered on either side by the lateral nail folds (paronychium). The nail plate is composed of hard, keratinized, squamous cells that are loosely adherent to germinal matrix but strongly attached to the sterile matrix. [] The nail fold, the most proximal aspect of the perionychium, is composed of a dorsal roof and a ventral floor.
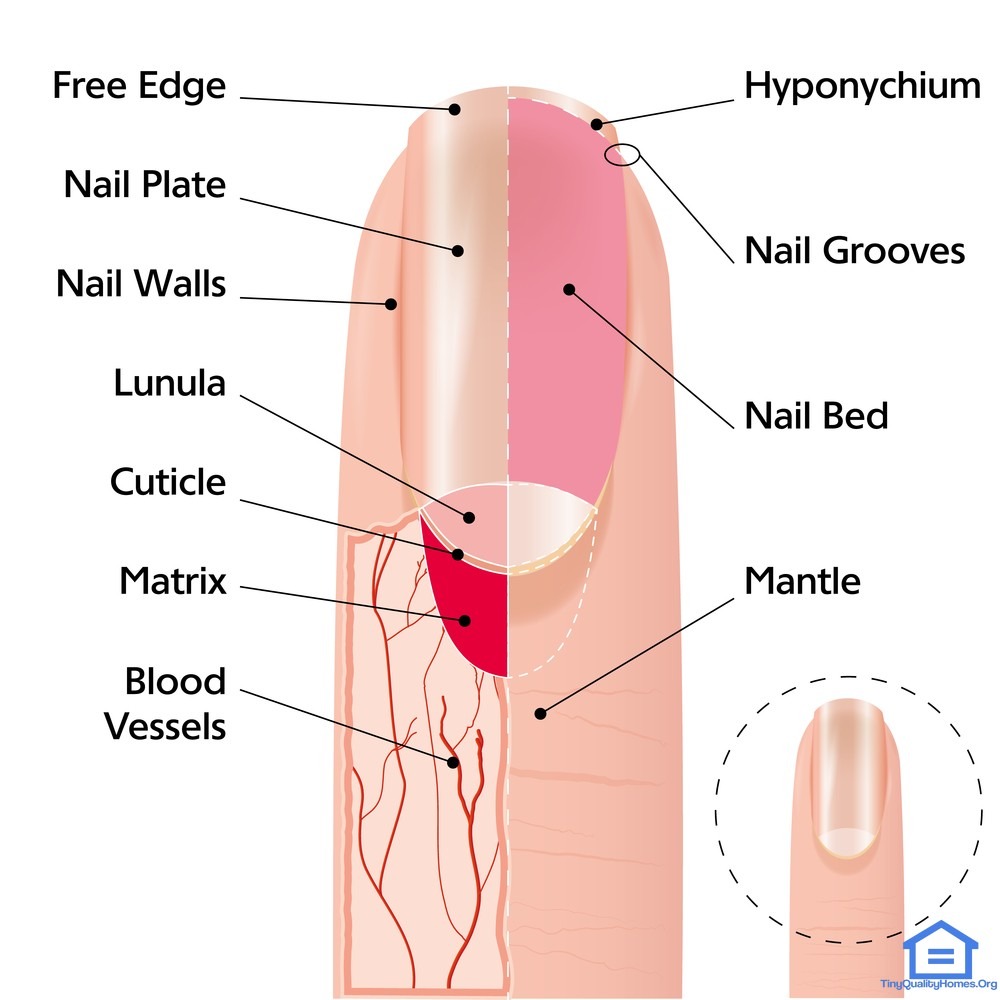
Nail Structure Women Fitness
Toenails A nail is a horn-like envelope covering the dorsal aspect of the terminal phalanges of fingers and toes in humans, most primates, and a few other mammals. Nails are similar to claws, which are found on numerous other animals. In common usage, the word nail often refers to the nail plate only.

The structure of a nail. nailtypes natural nail types Nail tech
The bottom diagram shows internal structures in a cross-section of the nail and nail bed. A nail has three main parts: the root, plate, and free margin. Other structures around or under the nail include the nail bed, cuticle, and nail fold. These structures are shown in Figure 10.6.2. The nail root
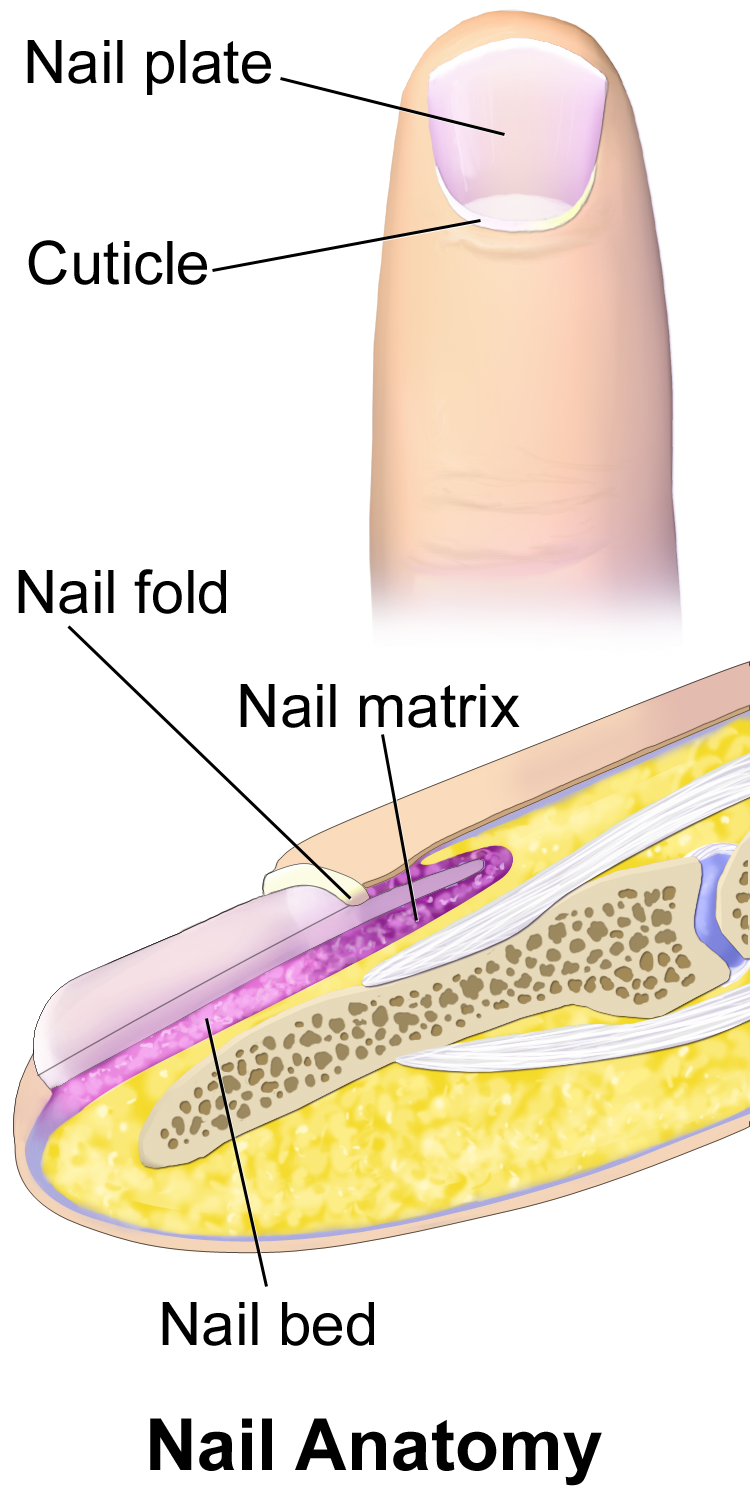
10.6 Nails Human Biology
A thin layer of skin, known as the cuticle, grows over the nail there. How do nails grow? At the proximal nail fold, the nail is tucked into a pouch in the skin. This area is referred to as the matrix. If you look at a nail, you will see a light half-moon-shaped area shimmering through the nail plate at the base of the nail.
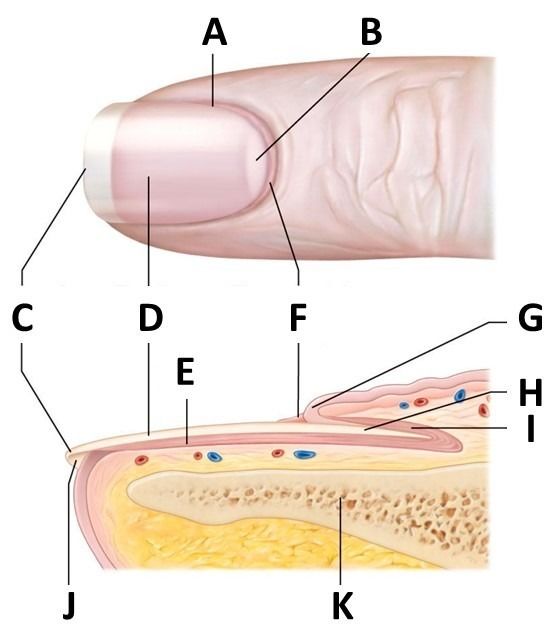
Nail and Structure Quiz
Lunula A bluish-white, opaque area that is visible through the nail plate. This area is the front part of the nail matrix. Sometimes, it's called the "moon." The lunula is the front part of the matrix we can see, or in other words, the visible matrix. Not all fingers have a visible lunula.

Ingrown Toenail Causes & How To Treat and Fix Infected Ingrown Toenail
Learn about Nail Structure by using a clear Nail Diagram
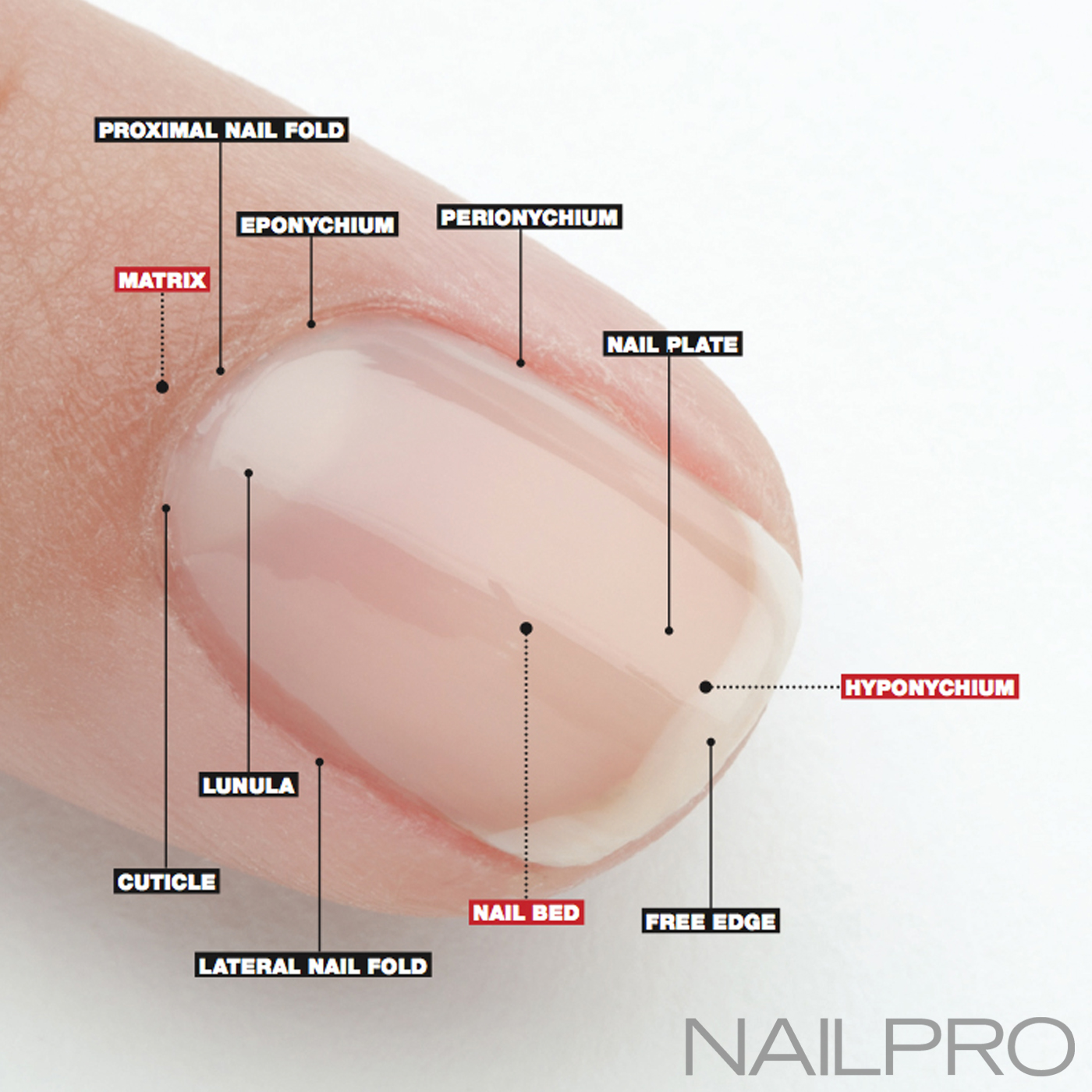
Nail Anatomy A Professional Primer on the Parts of the Nail
Here, a refresher on the essential parts of the nail, from base to tip and everything in between. Located beneath the skin at the nail's base, the matrix contains nerves and blood and lymph vessels that produce nail cells. The new cells flatten and are pushed forward toward the fingertip resulting in nail growth.

Exam 1 (informal study guide) Biology Biol&241 with Dr. Vega at Lake
In this video we discuss the structure of fingernails and toenails. We cover the different parts of nails and how nails grow. We also discuss some of the f.
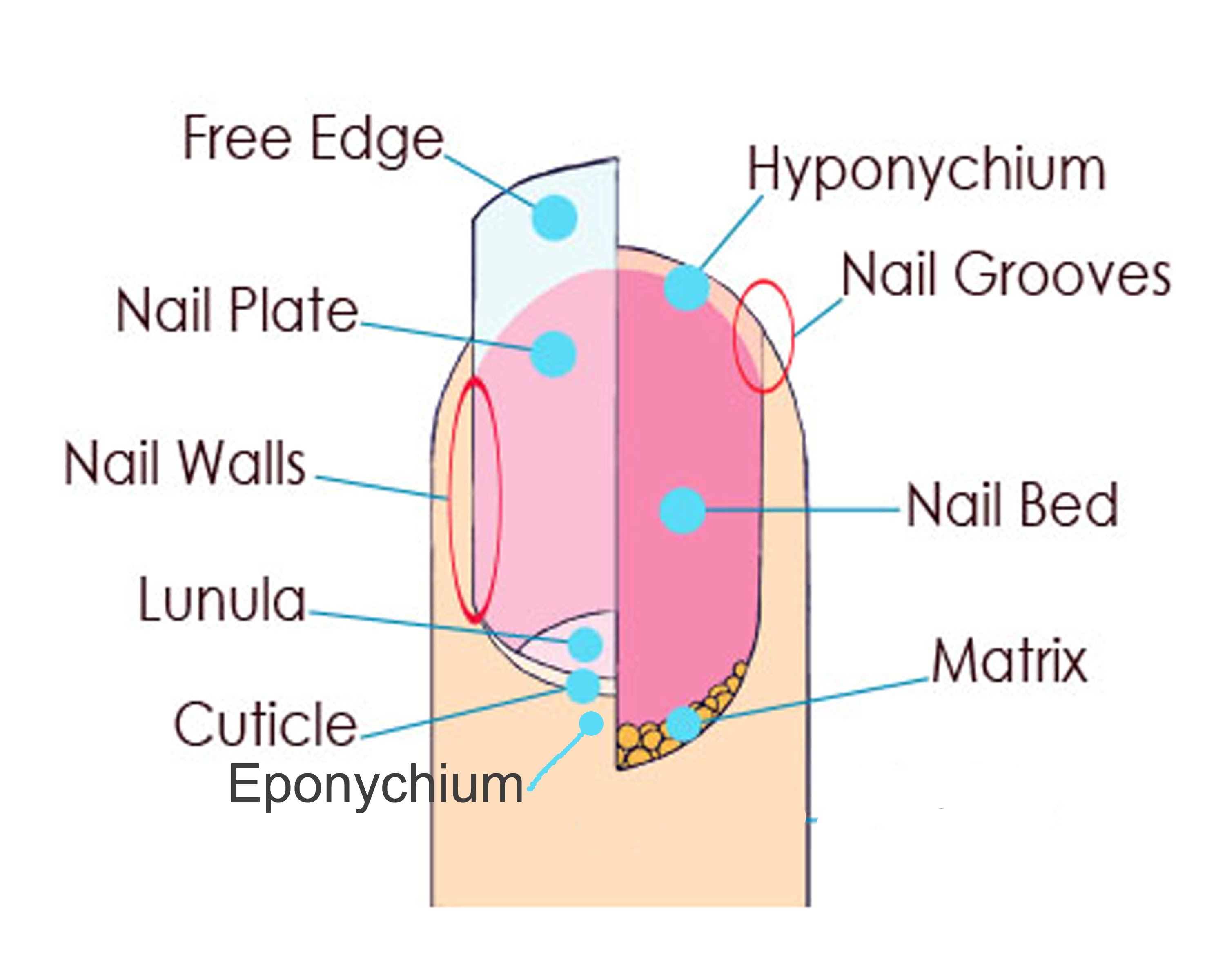
Manicure The Ontario Nail Institute
Figure 1. The nail is an accessory structure of the integumentary system. In addition, the nail body forms a back-support for picking up small objects with the fingers. The nail body is composed of densely packed dead keratinocytes. The epidermis in this part of the body has evolved a specialized structure upon which nails can form.

Nail Anatomy (and why you should know it)
Lunula Visible Part of the matrix that extends from underneath the living skin; it is whitish, half-moon shaped at the base of the nail. Cuticle Dead, colorless tissue attached to the natural nail plate. Mantle. Matrix Area where the nail plate cells are formed;this area composed of matrix cells that produce the nail plate. Nail Bed
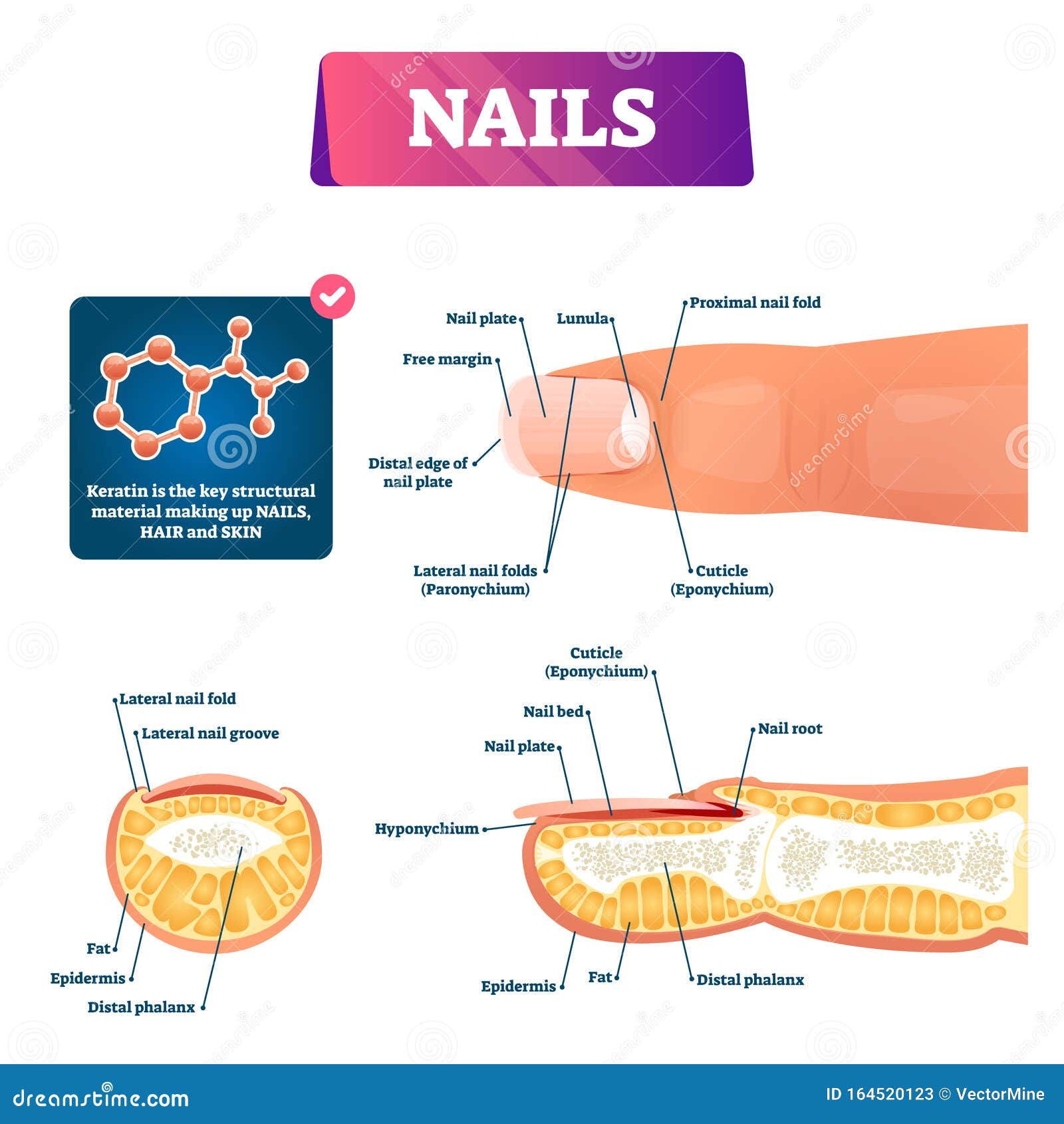
Nail Anatomy Structure Diagram, Vector Illustration Stock Vector
Anatomy of the Nails. The nail bed is a specialized structure of the epidermis that is found at the tips of our fingers and toes.. Above: Illustrated diagram of the anatomy of a fingernail. Above: Microscopic images of a fingernail cross section. The top image is magnified by 4x and the bottom image is the same tissue sample as the top image.
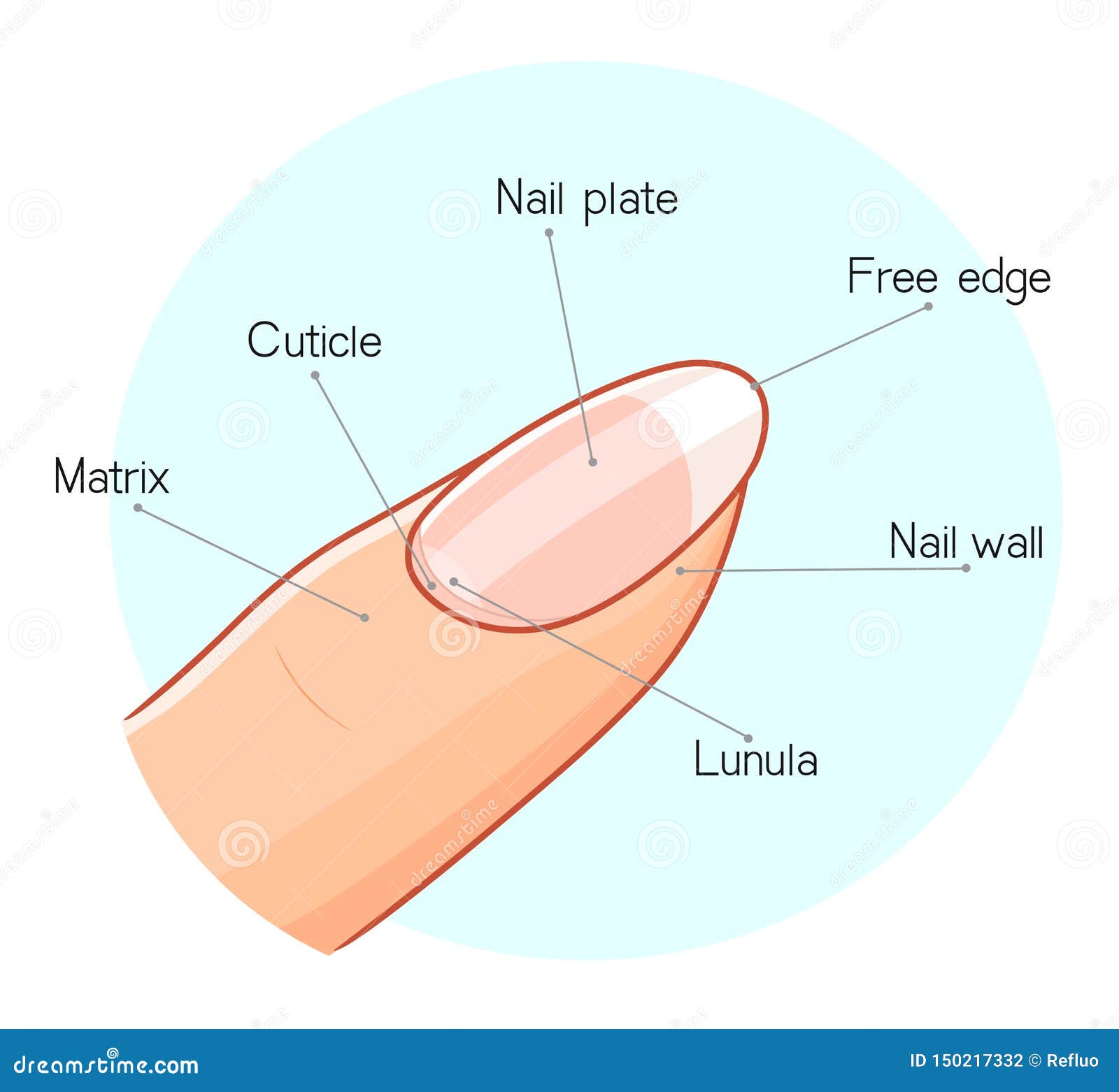
Nail Structure Illustration Stock Vector Illustration of clean
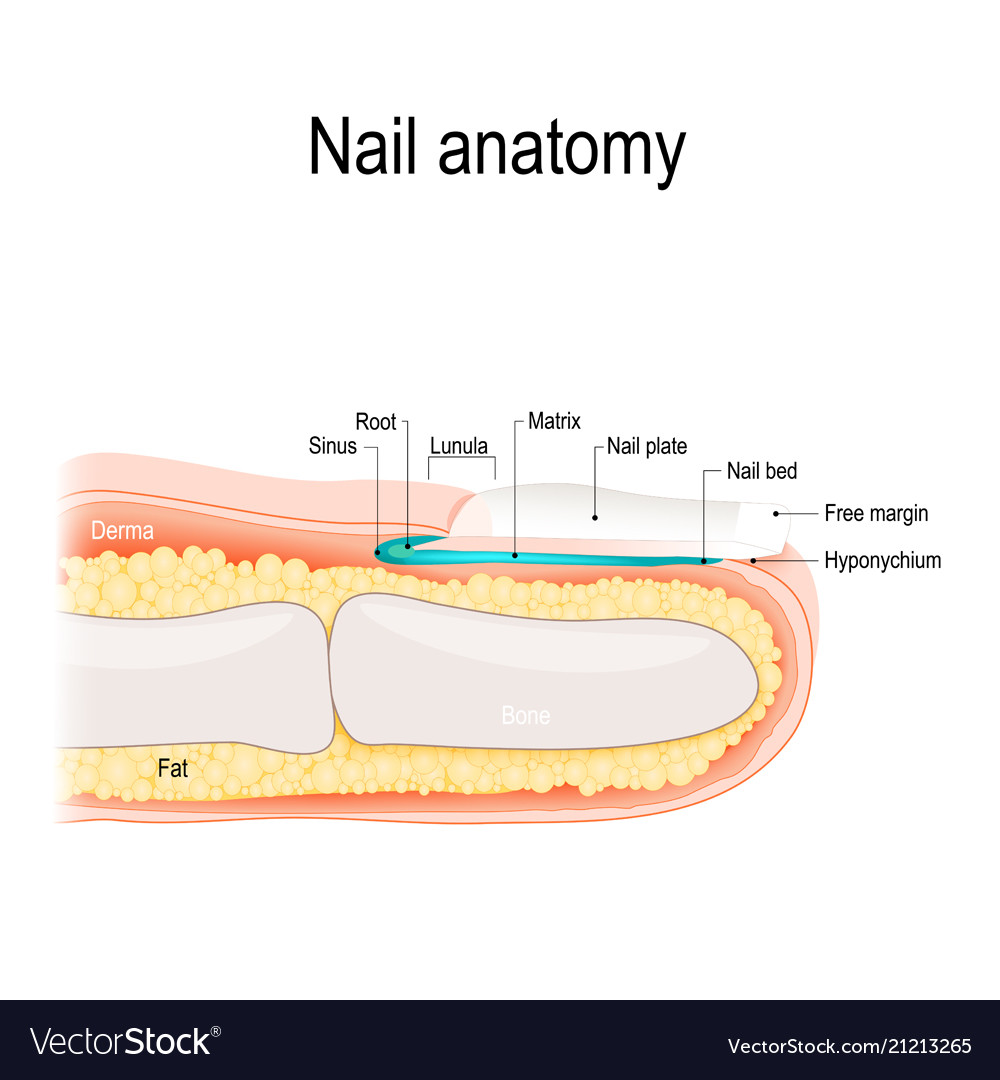
Structure A. Nail plate; B. lunula; C. root; D. sinus; E. matrix; F. nail bed; G. hyponychium; H. free margin. The nail consists of the nail plate, the nail matrix and the nail bed below it, and the grooves surrounding it. [2] Parts of the nail The nail matrix is the active tissue (or germinal matrix) that generates cells.
Anatomy Of Nail Anatomy Drawing Diagram
Diagram Nail bed anatomy Medical conditions Diagnosis Summary What is nail matrix? The nail matrix is the area where your fingernails and toenails start to grow. The matrix creates new.